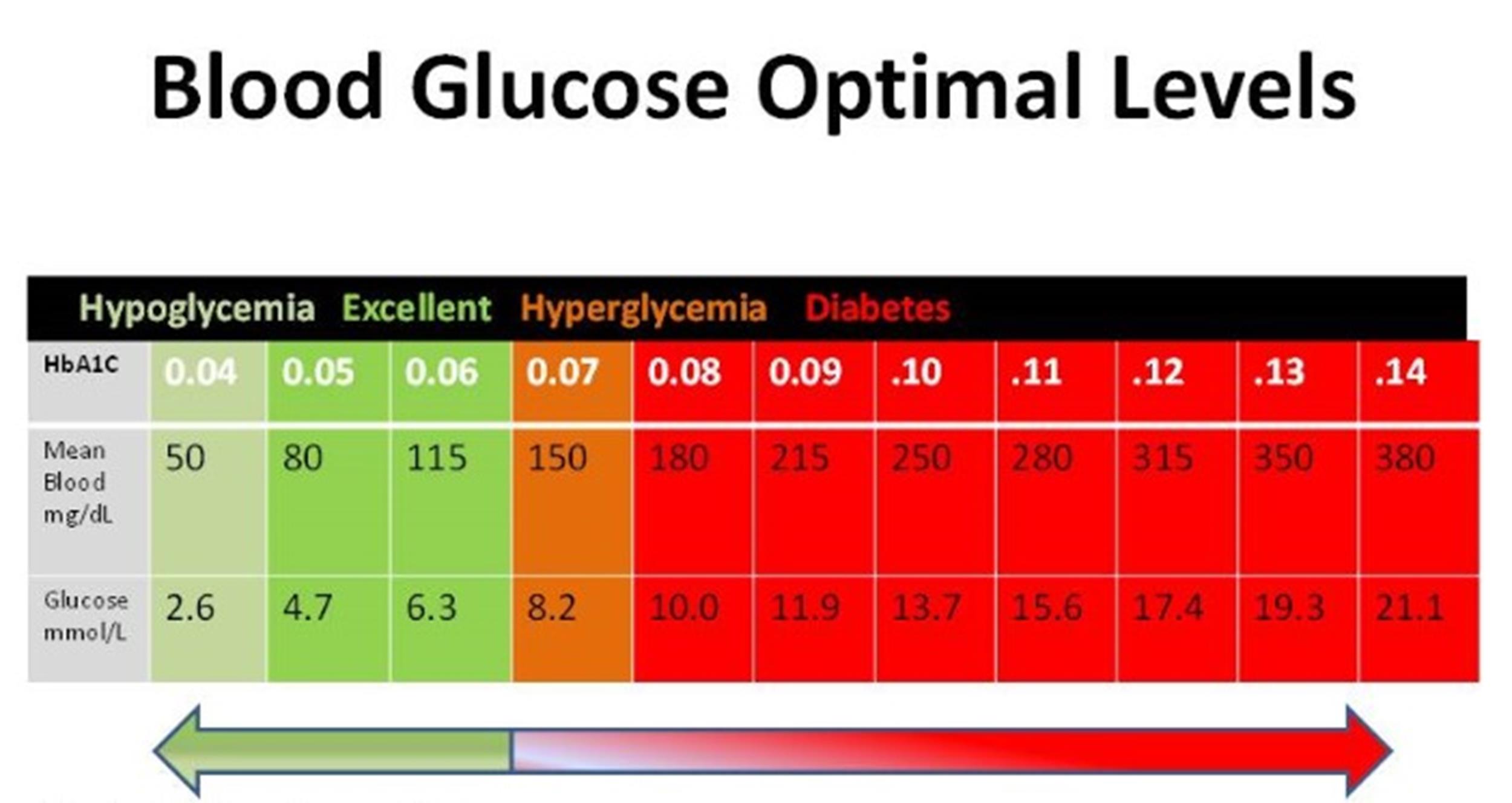
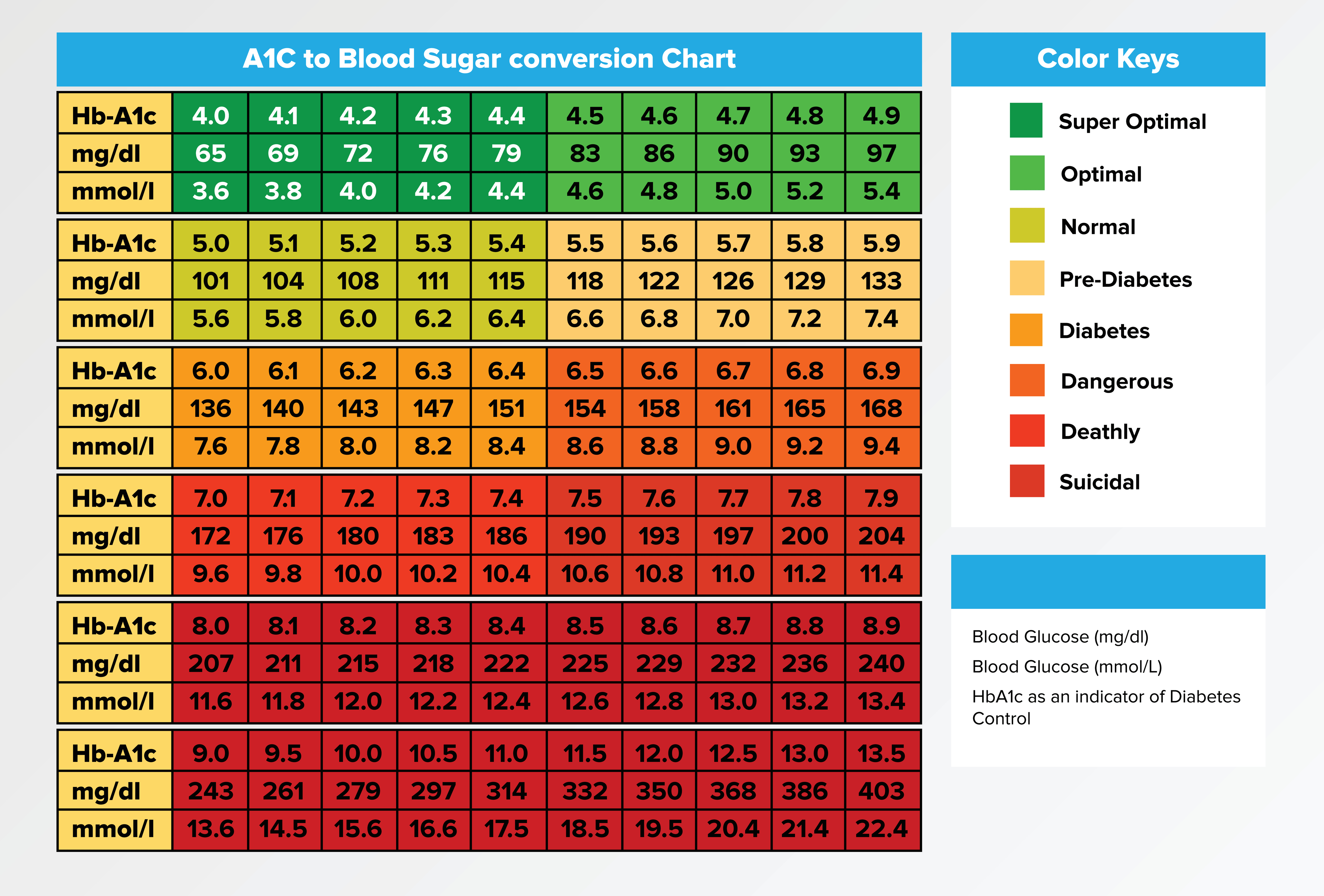
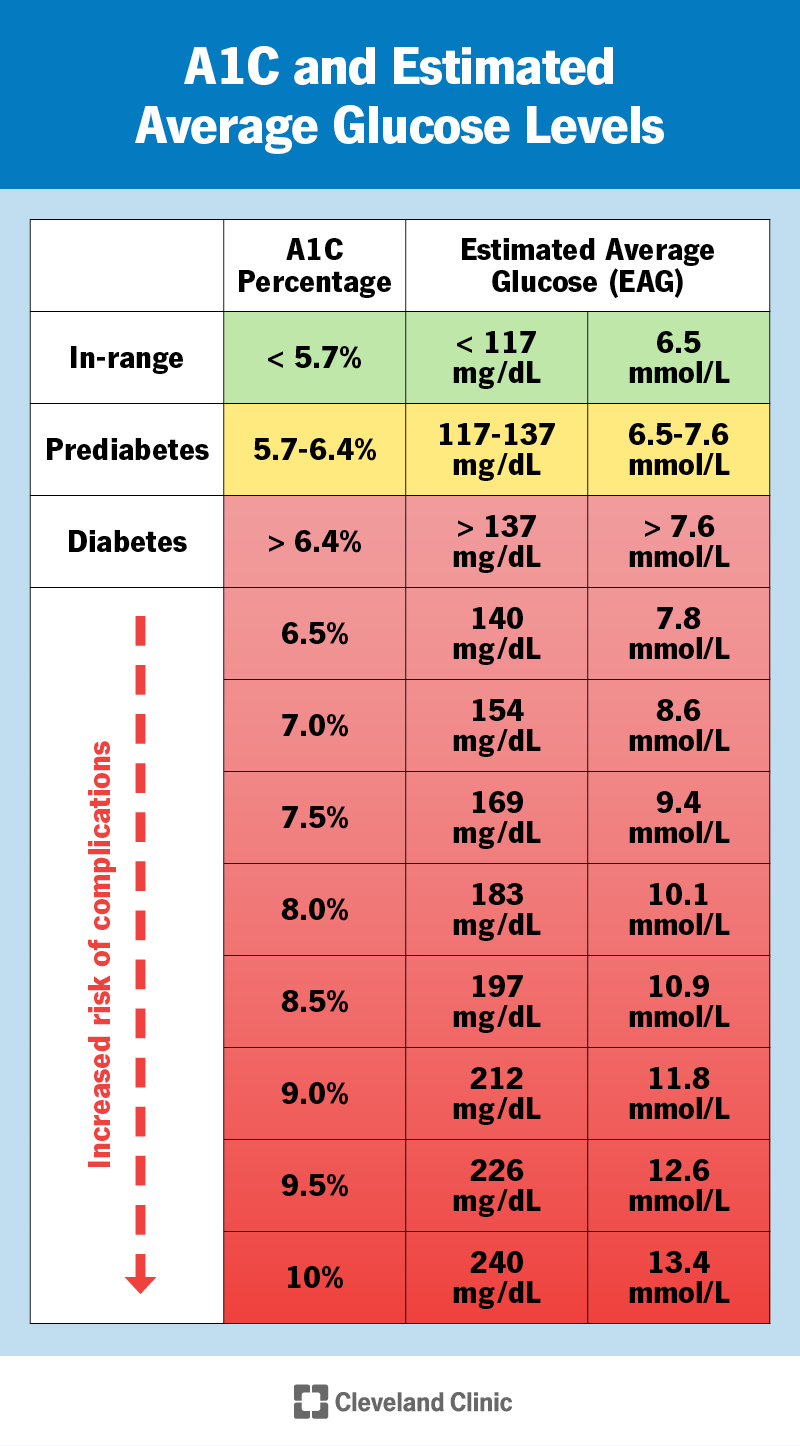
A1C During Pregnancy
A1C During Pregnancy - Additionally, as a1c represents an integrated measure of glucose, it may not fully capture postprandial. <6% (42 mmol/mol) may be optimal if this can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia, but the target may be relaxed to <7% (53 mmol/mol) if necessary to. 3 these targets may be different. Class a2gdm refers to the clinical scenario where. Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close to normal as possible—ideally below 6.5 percent—before getting pregnant. 3 after the first 3 months of pregnancy, your target may be as low as 6 percent. And no matter what your a1c is, taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid early will lower your child’s risk of birth defects. Acog released updated guidance on gestational diabetes (gdm), which has become increasingly prevalent worldwide. This is also the time to make sure you have the right health care providers lined up for your care during your. Due to physiological increases in red blood cell turnover, a1c levels fall during normal pregnancy (36,37).
Additionally, as a1c represents an integrated measure of glucose, it may not fully capture postprandial. And no matter what your a1c is, taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid early will lower your child’s risk of birth defects. Class a2gdm refers to the clinical scenario where. Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close to normal as possible—ideally below 6.5 percent—before getting pregnant. Acog released updated guidance on gestational diabetes (gdm), which has become increasingly prevalent worldwide. Due to physiological increases in red blood cell turnover, a1c levels fall during normal pregnancy (36,37). This is also the time to make sure you have the right health care providers lined up for your care during your. <6% (42 mmol/mol) may be optimal if this can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia, but the target may be relaxed to <7% (53 mmol/mol) if necessary to. 3 these targets may be different. 3 after the first 3 months of pregnancy, your target may be as low as 6 percent.
Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close to normal as possible—ideally below 6.5 percent—before getting pregnant. And no matter what your a1c is, taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid early will lower your child’s risk of birth defects. Class a2gdm refers to the clinical scenario where. <6% (42 mmol/mol) may be optimal if this can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia, but the target may be relaxed to <7% (53 mmol/mol) if necessary to. 3 these targets may be different. Due to physiological increases in red blood cell turnover, a1c levels fall during normal pregnancy (36,37). 3 after the first 3 months of pregnancy, your target may be as low as 6 percent. This is also the time to make sure you have the right health care providers lined up for your care during your. Additionally, as a1c represents an integrated measure of glucose, it may not fully capture postprandial. Acog released updated guidance on gestational diabetes (gdm), which has become increasingly prevalent worldwide.
A1C Printable Chart Printable Word Searches
Class a2gdm refers to the clinical scenario where. And no matter what your a1c is, taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid early will lower your child’s risk of birth defects. 3 after the first 3 months of pregnancy, your target may be as low as 6 percent. Acog released updated guidance on gestational diabetes (gdm), which has become increasingly prevalent.
Hyperglycemia Chart
Acog released updated guidance on gestational diabetes (gdm), which has become increasingly prevalent worldwide. <6% (42 mmol/mol) may be optimal if this can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia, but the target may be relaxed to <7% (53 mmol/mol) if necessary to. Class a2gdm refers to the clinical scenario where. 3 after the first 3 months of pregnancy, your target may.
A1c Printable Chart
Class a2gdm refers to the clinical scenario where. Acog released updated guidance on gestational diabetes (gdm), which has become increasingly prevalent worldwide. Additionally, as a1c represents an integrated measure of glucose, it may not fully capture postprandial. 3 these targets may be different. Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close to normal as possible—ideally below 6.5.
A Mean A1C () by treatment group during pregnancy and at the
And no matter what your a1c is, taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid early will lower your child’s risk of birth defects. Acog released updated guidance on gestational diabetes (gdm), which has become increasingly prevalent worldwide. 3 after the first 3 months of pregnancy, your target may be as low as 6 percent. This is also the time to make.
A1c Calculator And A1c Conversion Chart Geriatric Academy
3 after the first 3 months of pregnancy, your target may be as low as 6 percent. Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close to normal as possible—ideally below 6.5 percent—before getting pregnant. This is also the time to make sure you have the right health care providers lined up for your care during your. Acog.
A1c Levels Chart amulette
Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close to normal as possible—ideally below 6.5 percent—before getting pregnant. This is also the time to make sure you have the right health care providers lined up for your care during your. <6% (42 mmol/mol) may be optimal if this can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia, but the target may.
The Importance Of Monitoring A1c Levels During Pregnancy ShunChild
Acog released updated guidance on gestational diabetes (gdm), which has become increasingly prevalent worldwide. Due to physiological increases in red blood cell turnover, a1c levels fall during normal pregnancy (36,37). Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close to normal as possible—ideally below 6.5 percent—before getting pregnant. Additionally, as a1c represents an integrated measure of glucose, it.
Top 9 what is a dangerous level of a1c 2023
And no matter what your a1c is, taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid early will lower your child’s risk of birth defects. <6% (42 mmol/mol) may be optimal if this can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia, but the target may be relaxed to <7% (53 mmol/mol) if necessary to. Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close.
Hemoglobin A1c Levels During Pregnancy and Risk of Autism Spectrum
This is also the time to make sure you have the right health care providers lined up for your care during your. And no matter what your a1c is, taking prenatal vitamins with folic acid early will lower your child’s risk of birth defects. Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close to normal as possible—ideally below.
(PDF) Frequent Monitoring of A1C During Pregnancy as a Treatment Tool
<6% (42 mmol/mol) may be optimal if this can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia, but the target may be relaxed to <7% (53 mmol/mol) if necessary to. This is also the time to make sure you have the right health care providers lined up for your care during your. And no matter what your a1c is, taking prenatal vitamins with.
3 After The First 3 Months Of Pregnancy, Your Target May Be As Low As 6 Percent.
This is also the time to make sure you have the right health care providers lined up for your care during your. Class a2gdm refers to the clinical scenario where. 3 these targets may be different. Acog released updated guidance on gestational diabetes (gdm), which has become increasingly prevalent worldwide.
And No Matter What Your A1C Is, Taking Prenatal Vitamins With Folic Acid Early Will Lower Your Child’s Risk Of Birth Defects.
Most women with diabetes should aim for an a1c as close to normal as possible—ideally below 6.5 percent—before getting pregnant. <6% (42 mmol/mol) may be optimal if this can be achieved without significant hypoglycemia, but the target may be relaxed to <7% (53 mmol/mol) if necessary to. Due to physiological increases in red blood cell turnover, a1c levels fall during normal pregnancy (36,37). Additionally, as a1c represents an integrated measure of glucose, it may not fully capture postprandial.