Axiom In Math
Axiom In Math - Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. There are five basic axioms of algebra. An axiom serves as the base. Learn what axioms and proofs are in mathematics, and how they are used to build up a network of theorems. The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom and. There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division texts, called an axiom (or, in some texts, a postulate). Explore the examples of set theory.
Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Learn what axioms and proofs are in mathematics, and how they are used to build up a network of theorems. Explore the examples of set theory. An axiom serves as the base. There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division texts, called an axiom (or, in some texts, a postulate). There are five basic axioms of algebra. The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom and.
Explore the examples of set theory. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. There are five basic axioms of algebra. There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division texts, called an axiom (or, in some texts, a postulate). The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom and. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Learn what axioms and proofs are in mathematics, and how they are used to build up a network of theorems. An axiom serves as the base.
Discrete Mathematics Chapter 1 Logic and proofs 1282020
The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom and. Explore the examples of set theory. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem.
What is an axiom?
The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom and. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. Explore the examples of set theory. There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division texts, called an axiom (or, in some.
PPT Axiomatic Systems PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4520354
There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division texts, called an axiom (or, in some texts, a postulate). Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. Learn what axioms and proofs are in mathematics, and how they are used to build up.
Role of Axiomatization in Math & Math Ed Axiom Mathematical Proof
There are five basic axioms of algebra. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. Explore the examples of set theory. The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom and. There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division.
Solved What axiom can justify this statement 9* (8+5)=(9* 8)+(9* 5
The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom and. An axiom serves as the base. Learn what axioms and proofs are in mathematics, and how they are used to build up a network of theorems. There are five basic axioms of algebra. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without.
What is an axiom?
There are five basic axioms of algebra. There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division texts, called an axiom (or, in some texts, a postulate). Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom is a statement that is true or.
What is an Axiom Definition of Axiom
An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. An axiom serves as the base. The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom and. Explore the examples of set theory. Learn what axioms and proofs are in mathematics, and how they are used.
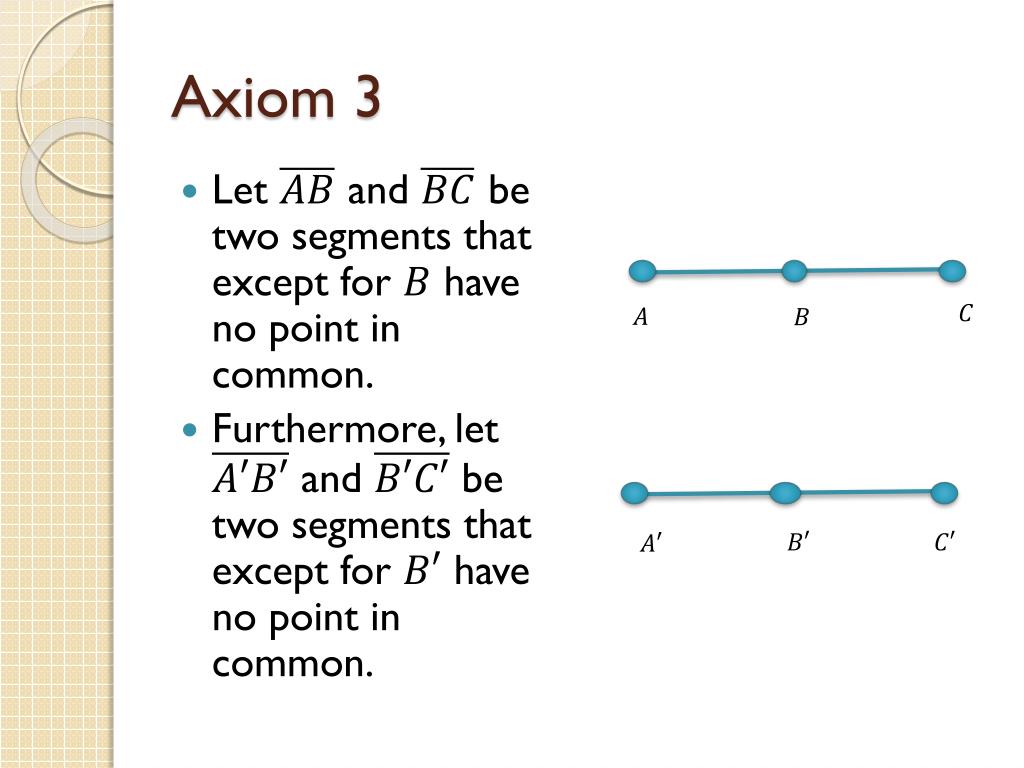
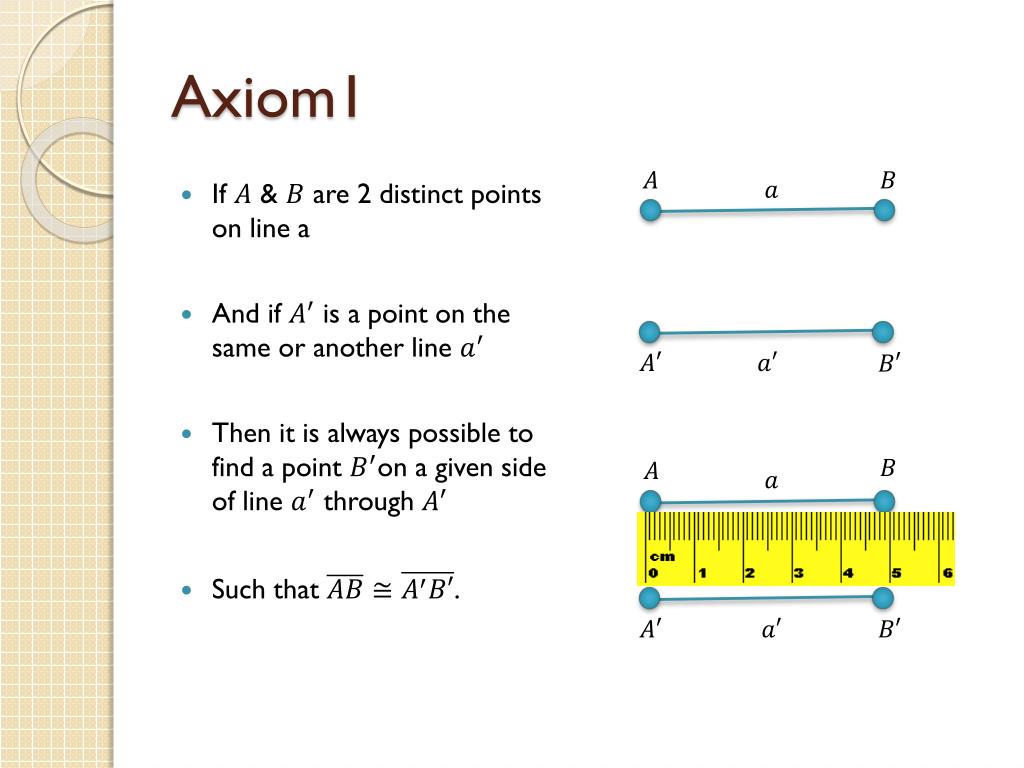
PPT Hilbert’s Axioms for Euclidean Geometry Axioms of Congruence
There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division texts, called an axiom (or, in some texts, a postulate). An axiom serves as the base. The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom and. Learn what axioms and proofs are in mathematics, and how they are used to build up a network.
PPT Hilbert’s Axioms for Euclidean Geometry Axioms of Congruence
Explore the examples of set theory. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Learn what axioms and proofs are in mathematics, and how they are used to build up a network of theorems. The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive axiom, additive axiom.
Axiom / Vanda Math notebook 80 lvs ( 5 in 1 pack) Shopee Philippines
Explore the examples of set theory. There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division texts, called an axiom (or, in some texts, a postulate). An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. The axioms are the reflexive axiom, symmetric axiom, transitive.
Learn What Axioms And Proofs Are In Mathematics, And How They Are Used To Build Up A Network Of Theorems.
An axiom serves as the base. There is a strange creature in mathematics, not typically mentioned in lower division texts, called an axiom (or, in some texts, a postulate). An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. There are five basic axioms of algebra.
The Axioms Are The Reflexive Axiom, Symmetric Axiom, Transitive Axiom, Additive Axiom And.
Explore the examples of set theory. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics.