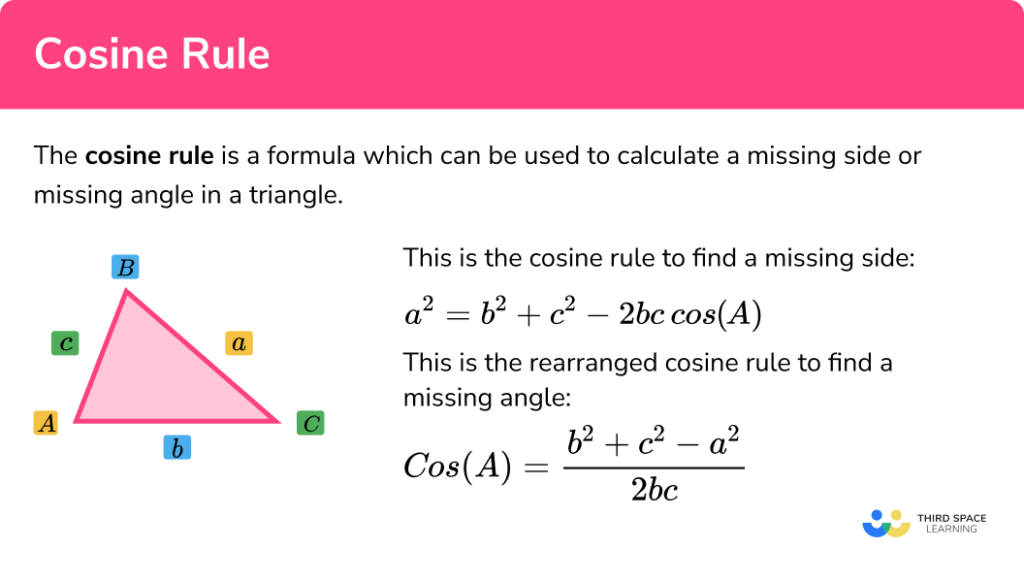
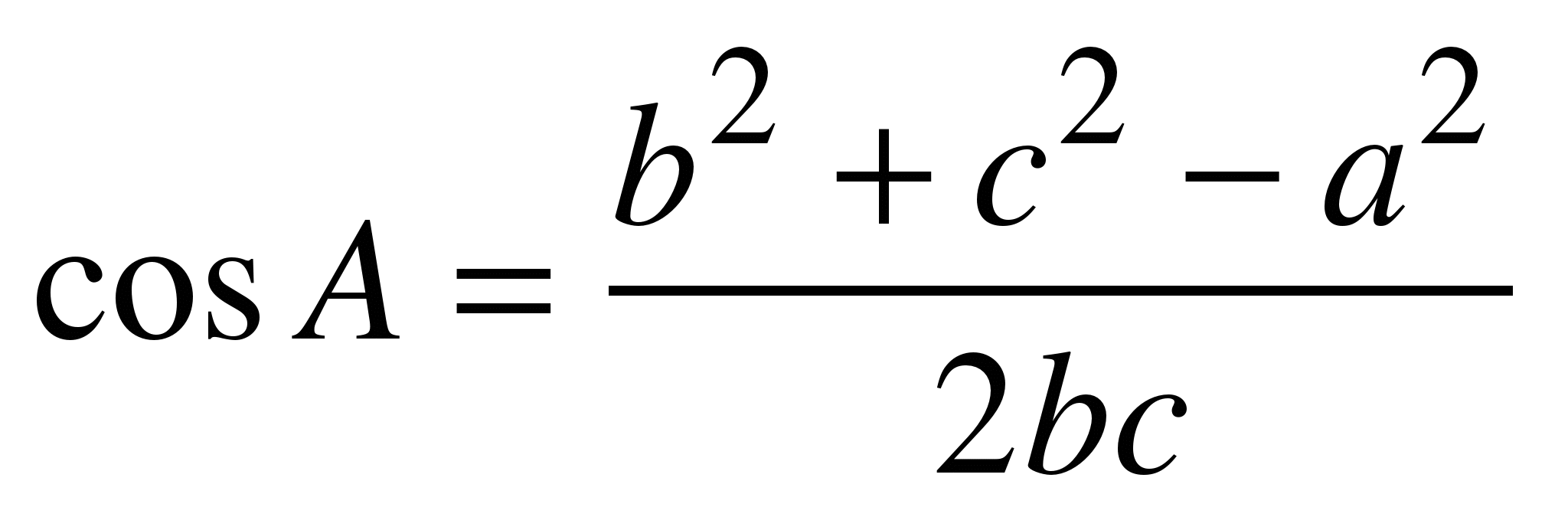Cosine Rule Formula
Cosine Rule Formula - Cosine law in trigonometry generalizes the pythagoras theorem. The law of cosines (alternatively the cosine formula or cosine rule) describes the relationship between the lengths of a triangle's sides and the cosine of its angles. The law of cosines (also called the cosine rule) says: In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. C 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos(c) it helps us solve some triangles. It can be rearranged to: It can be applied to. Let's see how to use it. Understand the cosine rule using.
In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. It can be rearranged to: Understand the cosine rule using. Cosine law in trigonometry generalizes the pythagoras theorem. Let's see how to use it. The law of cosines (also called the cosine rule) says: It can be applied to. C 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos(c) it helps us solve some triangles. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. The law of cosines (alternatively the cosine formula or cosine rule) describes the relationship between the lengths of a triangle's sides and the cosine of its angles.
Let's see how to use it. It can be rearranged to: The law of cosines (alternatively the cosine formula or cosine rule) describes the relationship between the lengths of a triangle's sides and the cosine of its angles. Cosine law in trigonometry generalizes the pythagoras theorem. Understand the cosine rule using. C 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos(c) it helps us solve some triangles. In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. The law of cosines (also called the cosine rule) says: It can be applied to.
the Cosine Rule National 5 Maths
Understand the cosine rule using. It can be applied to. It can be rearranged to: Cosine law in trigonometry generalizes the pythagoras theorem. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles.
Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
Understand the cosine rule using. C 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos(c) it helps us solve some triangles. The law of cosines (also called the cosine rule) says: The law of cosines (alternatively the cosine formula or cosine rule) describes the relationship between the lengths of a triangle's sides and the cosine of its angles. Let's.
The Cosine Rule Teaching Resources
The law of cosines (alternatively the cosine formula or cosine rule) describes the relationship between the lengths of a triangle's sides and the cosine of its angles. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Let's see how to use it. Understand the cosine rule using. Cosine.
Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
C 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos(c) it helps us solve some triangles. The law of cosines (also called the cosine rule) says: It can be rearranged to: Cosine law in trigonometry generalizes the pythagoras theorem. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its.
Cosine Rule & When to Use Them YouTube
C 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos(c) it helps us solve some triangles. Let's see how to use it. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Understand the cosine rule using. It can be rearranged to:
Cosine Rule GCSE Maths Steps, Examples & Worksheet
It can be applied to. C 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos(c) it helps us solve some triangles. In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. It can be rearranged to: The.
Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
The law of cosines (also called the cosine rule) says: Understand the cosine rule using. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. It can be applied to. C 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos(c) it helps us solve some triangles.
Law of Cosine (Cosine Law) with Examples and Proof Teachoo
The law of cosines (alternatively the cosine formula or cosine rule) describes the relationship between the lengths of a triangle's sides and the cosine of its angles. Cosine law in trigonometry generalizes the pythagoras theorem. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. The law of cosines.
The Cosine Rule IGCSE at Mathematics Realm
Cosine law in trigonometry generalizes the pythagoras theorem. The law of cosines (also called the cosine rule) says: Let's see how to use it. The law of cosines relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. It can be applied to.
The Law Of Cosines Relates The Lengths Of The Sides Of A Triangle To The Cosine Of One Of Its Angles.
The law of cosines (alternatively the cosine formula or cosine rule) describes the relationship between the lengths of a triangle's sides and the cosine of its angles. Cosine law in trigonometry generalizes the pythagoras theorem. C 2 = a 2 + b 2 − 2ab cos(c) it helps us solve some triangles. It can be applied to.
It Can Be Rearranged To:
The law of cosines (also called the cosine rule) says: Understand the cosine rule using. In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula or cosine rule) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Let's see how to use it.