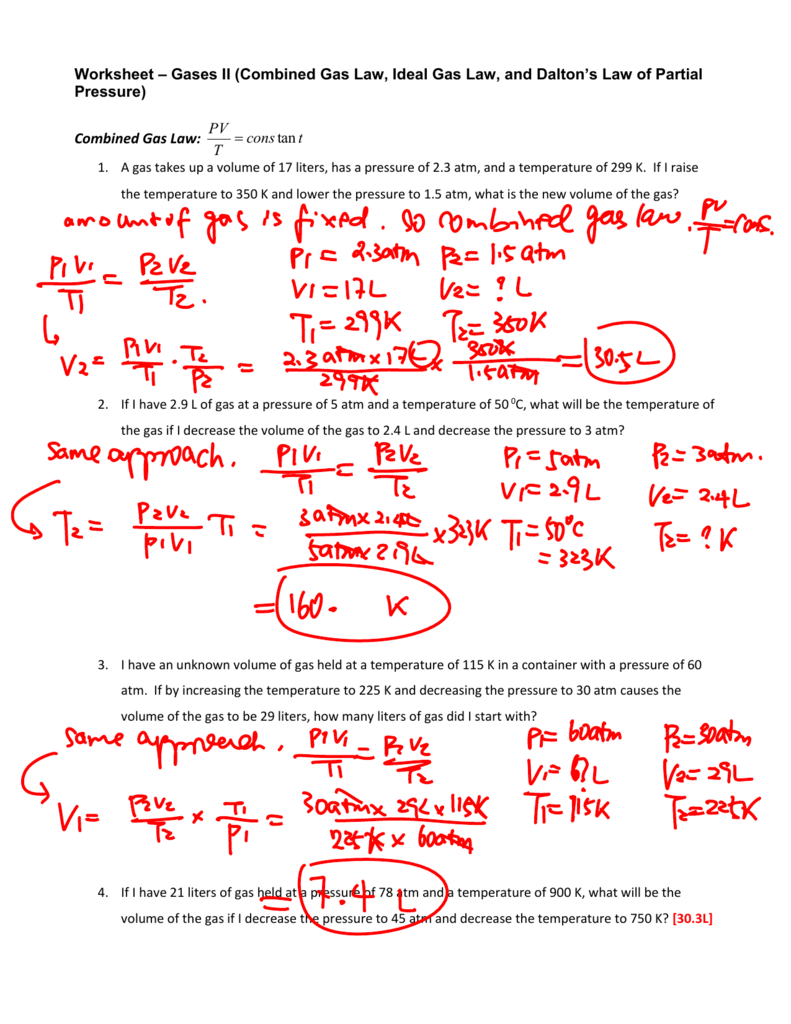
Ideal Gas Law Worksheet With Answers
Ideal Gas Law Worksheet With Answers - The ideal gas law states that pv=nrt, where p is the pressure of a gas, v is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles of gas present, r is the. How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a lung capacity of 3.9 l? 10 ideal gas law 1. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. On this worksheet you will practice with the ideal gas law, the combined gas law, as well as the relationships between the. The ideal gas law directions: Use your knowledge of the ideal and combined gas laws to solve the following problems. Solve each of the following problems.
The ideal gas law directions: Solve each of the following problems. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. Use your knowledge of the ideal and combined gas laws to solve the following problems. If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a lung capacity of 3.9 l? On this worksheet you will practice with the ideal gas law, the combined gas law, as well as the relationships between the. 10 ideal gas law 1. The ideal gas law states that pv=nrt, where p is the pressure of a gas, v is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles of gas present, r is the.
The ideal gas law states that pv=nrt, where p is the pressure of a gas, v is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles of gas present, r is the. How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a lung capacity of 3.9 l? On this worksheet you will practice with the ideal gas law, the combined gas law, as well as the relationships between the. 10 ideal gas law 1. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. Use your knowledge of the ideal and combined gas laws to solve the following problems. The ideal gas law directions: If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. Solve each of the following problems.
Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answer Key —
How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a lung capacity of 3.9 l? Solve each of the following problems. If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. Use your knowledge of the ideal and combined gas laws to solve the following problems. On this worksheet you will practice with.
Worksheet Gas Laws II Answers
10 ideal gas law 1. The ideal gas law states that pv=nrt, where p is the pressure of a gas, v is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles of gas present, r is the. Solve each of the following problems. How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a.
Ideal Gas Law Worksheet 2 Answer Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV = nRT Use
10 ideal gas law 1. On this worksheet you will practice with the ideal gas law, the combined gas law, as well as the relationships between the. The ideal gas law directions: Use your knowledge of the ideal and combined gas laws to solve the following problems. How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult.
20++ Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answers Worksheets Decoomo
If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a lung capacity of 3.9 l? 10 ideal gas law 1. Use your knowledge of the ideal and combined gas laws to solve the.
4 Ideal Gas Law Worksheet FabTemplatez
If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. Use your knowledge of the ideal and combined gas laws to solve the following problems. The ideal gas law directions: Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. The ideal gas law states that pv=nrt, where p is the pressure of a gas, v is the.
Solved Ideal Gas Law Practice Worksheet Solve the following
How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a lung capacity of 3.9 l? Solve each of the following problems. 10 ideal gas law 1. If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. On this worksheet you will practice with the ideal gas law, the combined gas law, as well.
Combined Gas Law Worksheet Answers Printable Word Searches
10 ideal gas law 1. If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. The ideal gas law directions: The ideal gas law states that pv=nrt, where p is the pressure of a gas, v is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles of gas present, r is the. Solve each of the.
30++ Combined Gas Law Worksheet Answer Key Worksheets Decoomo
Solve each of the following problems. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. 10 ideal gas law 1. How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a lung capacity of 3.9 l? On this worksheet you will practice with the ideal gas law, the combined gas law, as well as the.
30++ Gas Laws Worksheet 1 Answer Key Worksheets Decoomo
Use your knowledge of the ideal and combined gas laws to solve the following problems. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. Solve each of the following problems. On this worksheet you will practice with the ideal gas law, the combined gas law, as well as the relationships between the. If it involves moles or grams, it.
20++ Ideal Gas Law Worksheet Answers Worksheets Decoomo
Use your knowledge of the ideal and combined gas laws to solve the following problems. If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. 10 ideal gas law 1. Solve each of the following problems. How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a lung capacity of 3.9 l?
Use Your Knowledge Of The Ideal And Combined Gas Laws To Solve The Following Problems.
If it involves moles or grams, it must be pv = nrt. Show your work, including proper units, to earn full credit. Solve each of the following problems. How many moles of gas (air) are in the lungs of an adult with a lung capacity of 3.9 l?
10 Ideal Gas Law 1.
On this worksheet you will practice with the ideal gas law, the combined gas law, as well as the relationships between the. The ideal gas law states that pv=nrt, where p is the pressure of a gas, v is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles of gas present, r is the. The ideal gas law directions: