Vesicles Can Be Formed From The Blank Membrane
Vesicles Can Be Formed From The Blank Membrane - The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma. Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the. Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells.
Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the. Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma.
Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma. Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the.
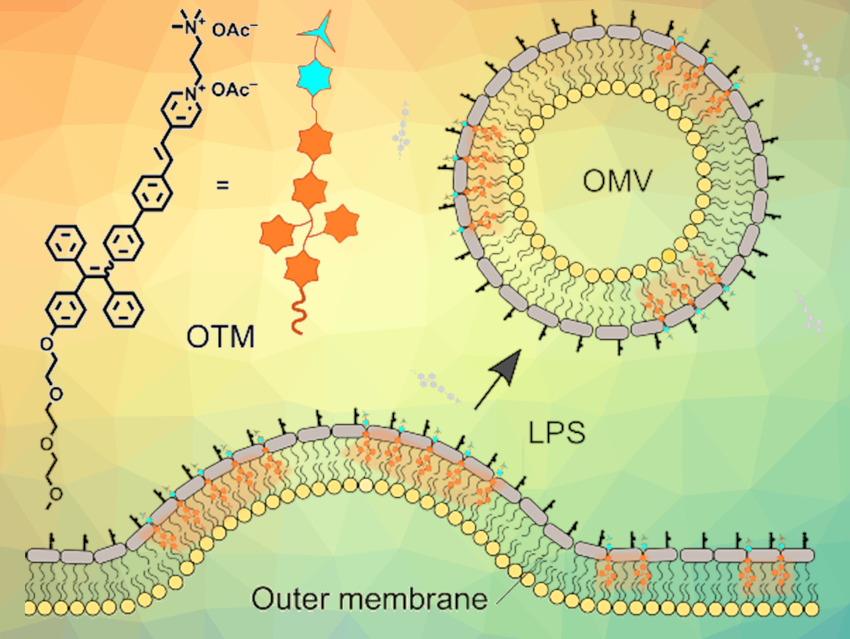
Efficient Detection of Outer Membrane Vesicles ChemistryViews
Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the. The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma.
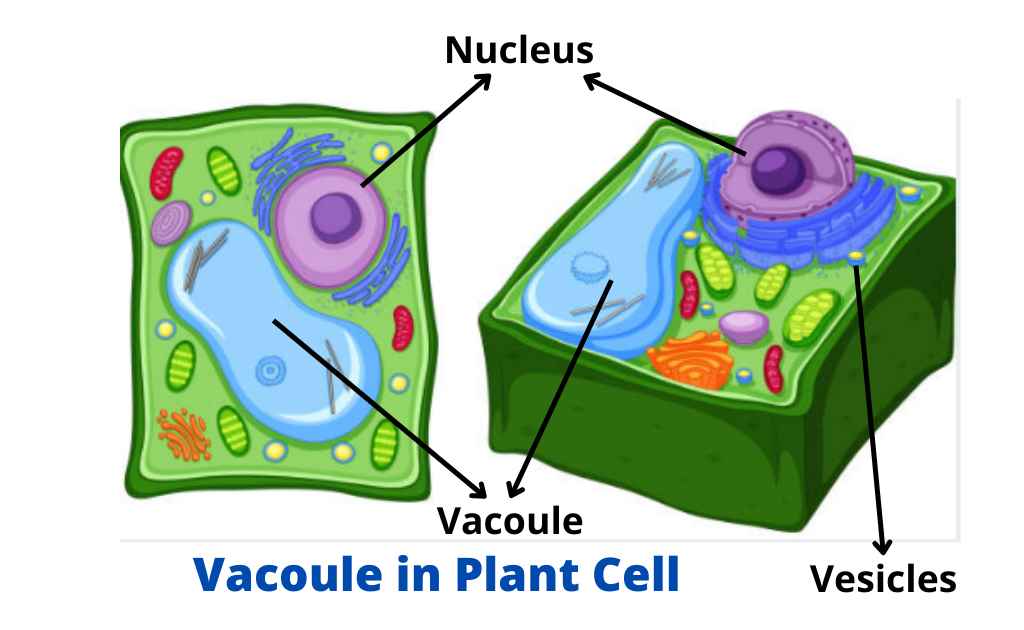
Vacuoles and Vesicles Definition, Structure, and Functions
Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma. Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the.
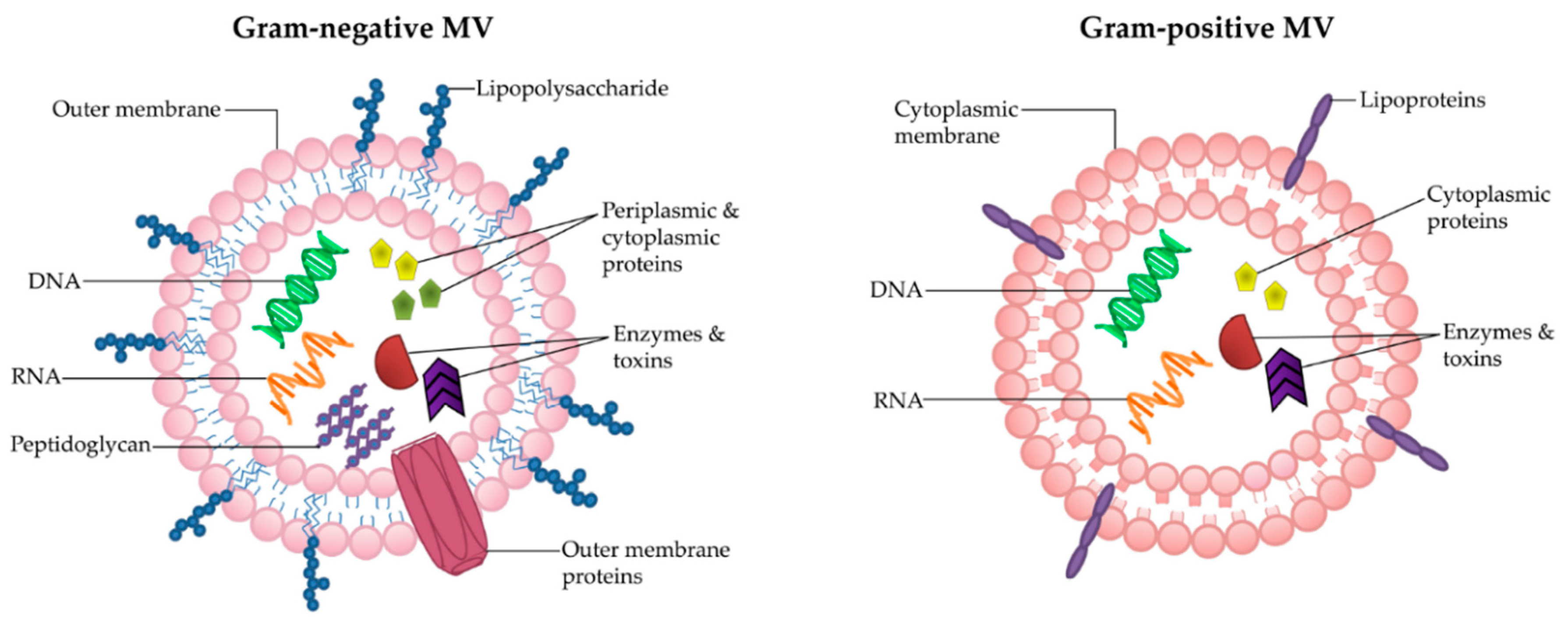
IJMS Free FullText The Therapeutic Benefit of Bacterial Membrane
Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the. The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma. Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells.
Cell Membrane Function and Structure
Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the. The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma.
Frontiers Outer membrane vesicles from bacteria Role and potential
Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the. Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma.
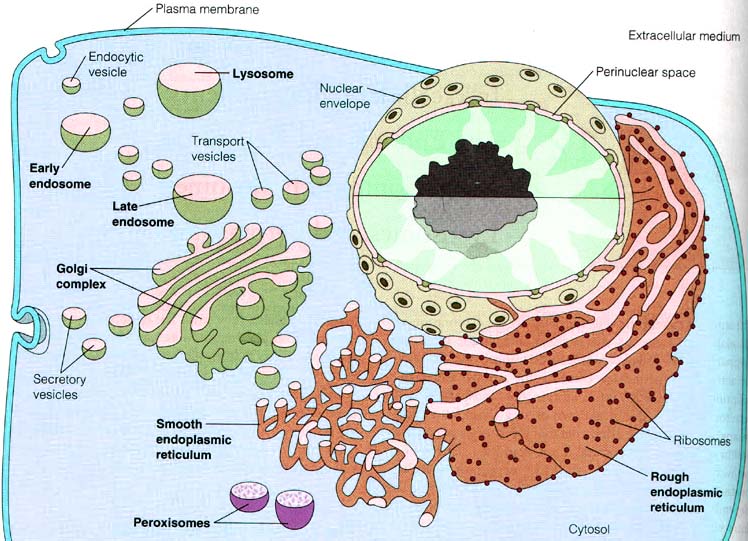
Vesicles Transport Information
Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the. Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma.
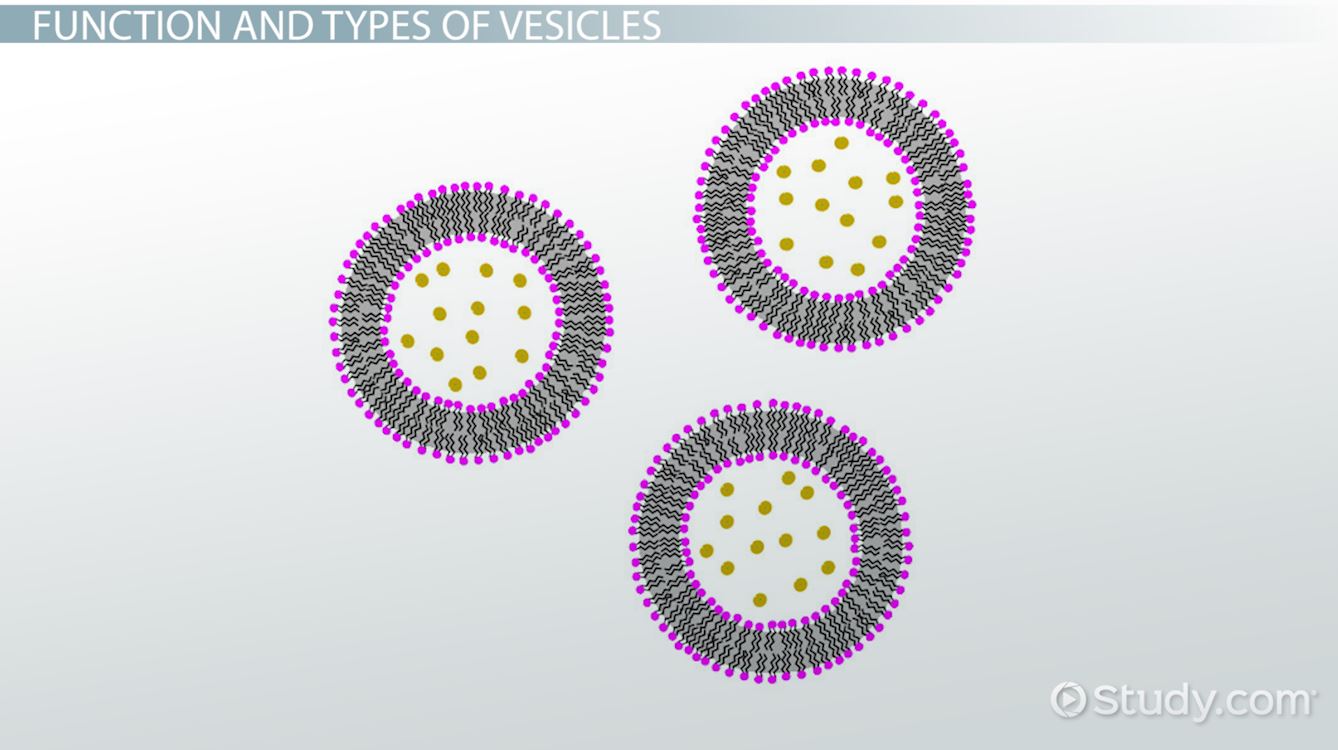
Vesicles Definition & Function Video & Lesson Transcript
The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma. Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the.
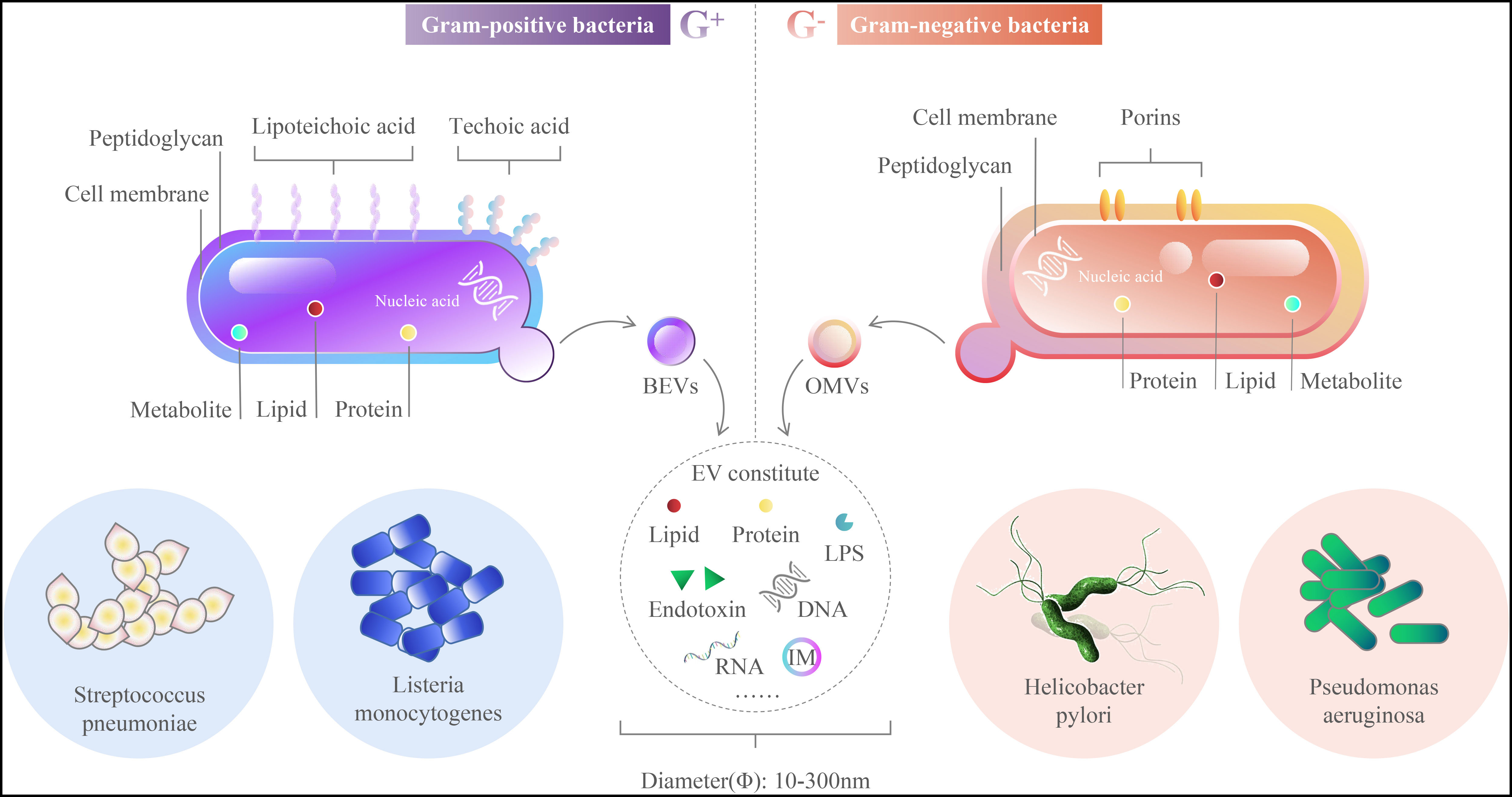
Formation of distinct bacterial membrane vesicles. Three major types of
The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma. Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the.
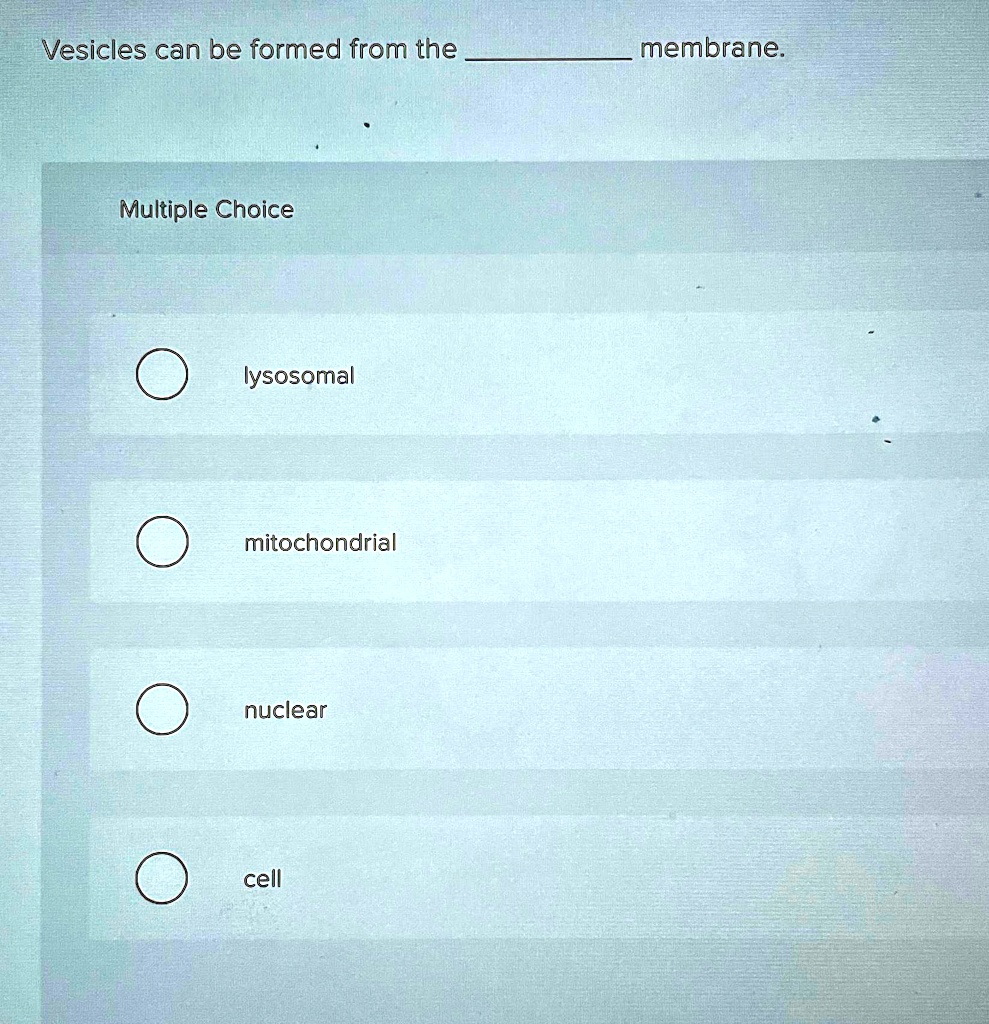
SOLVED Vesicles can be formed from the membrane. Multiple Choice
The vesicle is formed on the inside of the plasma. Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells. Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the.
The Vesicle Is Formed On The Inside Of The Plasma.
Extremely important for the movement of material within cells, vesicles are formed by membrane budding from organelles such as the. Vesicles can be formed by pinching off a small piece of the plasma membrane of cells.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png)